- Flutter 布局(九)- Flow、Table、Wrap详解
- 1. Flow
- 1.1 简介
- 1.2 布局行为
- 1.3 继承关系
- 1.4 示例代码
- 1.5 源码解析
- 1.5.1 属性解析
- 1.5.2 源码
- 1.6 使用场景
- 2. Table
- 2.1 简介
- 2.2 布局行为
- 2.3 继承关系
- 2.4 示例代码
- 2.5 源码解析
- 2.5.1 属性解析
- 2.5.2 源码
- 2.6 使用场景
- 3. Wrap
- 3.1 简介
- 3.2 布局行为
- 3.3 继承关系
- 3.4 示例代码
- 3.5 源码解析
- 3.5.1 属性解析
- 3.5.2 源码
- 3.6 使用场景
- 4. 后话
- 5. 参考
- 1. Flow
Flutter 布局(九)- Flow、Table、Wrap详解
本文主要介绍Flutter布局中的Flow、Table、Wrap控件,详细介绍了其布局行为以及使用场景,并对源码进行了分析。
1. Flow
A widget that implements the flow layout algorithm.
1.1 简介
Flow按照解释的那样,是一个实现流式布局算法的控件。流式布局在大前端是很常见的布局方式,但是一般使用Flow很少,因为其过于复杂,很多场景下都会去使用Wrap。
1.2 布局行为
Flow官方介绍是一个对child尺寸以及位置调整非常高效的控件,主要是得益于其FlowDelegate。另外Flow在用转换矩阵(transformation matrices)对child进行位置调整的时候进行了优化。
Flow以及其child的一些约束都会受到FlowDelegate的控制,例如重写FlowDelegate中的geiSize,可以设置Flow的尺寸,重写其getConstraintsForChild方法,可以设置每个child的布局约束条件。
Flow之所以高效,是因为其在定位过后,如果使用FlowDelegate中的paintChildren改变child的尺寸或者位置,只是重绘,并没有实际调整其位置。
1.3 继承关系
Object > Diagnosticable > DiagnosticableTree > Widget > RenderObjectWidget > MultiChildRenderObjectWidget > Flow
1.4 示例代码
const width = 80.0;const height = 60.0;Flow(delegate: TestFlowDelegate(margin: EdgeInsets.fromLTRB(10.0, 10.0, 10.0, 10.0)),children: <Widget>[new Container(width: width, height: height, color: Colors.yellow,),new Container(width: width, height: height, color: Colors.green,),new Container(width: width, height: height, color: Colors.red,),new Container(width: width, height: height, color: Colors.black,),new Container(width: width, height: height, color: Colors.blue,),new Container(width: width, height: height, color: Colors.lightGreenAccent,),],)class TestFlowDelegate extends FlowDelegate {EdgeInsets margin = EdgeInsets.zero;TestFlowDelegate({this.margin});@overridevoid paintChildren(FlowPaintingContext context) {var x = margin.left;var y = margin.top;for (int i = 0; i < context.childCount; i++) {var w = context.getChildSize(i).width + x + margin.right;if (w < context.size.width) {context.paintChild(i,transform: new Matrix4.translationValues(x, y, 0.0));x = w + margin.left;} else {x = margin.left;y += context.getChildSize(i).height + margin.top + margin.bottom;context.paintChild(i,transform: new Matrix4.translationValues(x, y, 0.0));x += context.getChildSize(i).width + margin.left + margin.right;}}}@overridebool shouldRepaint(FlowDelegate oldDelegate) {return oldDelegate != this;}}
样例其实并不复杂,FlowDelegate需要自己实现child的绘制,其实大多数时候就是位置的摆放。上面例子中,对每个child按照给定的margin值,进行排列,如果超出一行,则在下一行进行布局。

另外,对这个例子多做一个说明,对于上述child宽度的变化,这个例子是没问题的,如果每个child的高度不同,则需要对代码进行调整,具体的调整是换行的时候,需要根据上一行的最大高度来确定下一行的起始y坐标。
1.5 源码解析
构造函数如下:
Flow({Key key,@required this.delegate,List<Widget> children = const <Widget>[],})
1.5.1 属性解析
delegate:影响Flow具体布局的FlowDelegate。
其中FlowDelegate包含如下几个方法:
- getConstraintsForChild: 设置每个child的布局约束条件,会覆盖已有的;
- getSize:设置Flow的尺寸;
- paintChildren:child的绘制控制代码,可以调整尺寸位置,写起来比较的繁琐;
- shouldRepaint:是否需要重绘;
- shouldRelayout:是否需要重新布局。
其中,我们平时使用的时候,一般会使用到paintChildren以及shouldRepaint两个方法。
1.5.2 源码
我们先来看一下Flow的布局代码
Size _getSize(BoxConstraints constraints) {assert(constraints.debugAssertIsValid());return constraints.constrain(_delegate.getSize(constraints));}@overridevoid performLayout() {size = _getSize(constraints);int i = 0;_randomAccessChildren.clear();RenderBox child = firstChild;while (child != null) {_randomAccessChildren.add(child);final BoxConstraints innerConstraints = _delegate.getConstraintsForChild(i, constraints);child.layout(innerConstraints, parentUsesSize: true);final FlowParentData childParentData = child.parentData;childParentData.offset = Offset.zero;child = childParentData.nextSibling;i += 1;}}
可以看到Flow尺寸的取值,直接来自于delegate的getSize方法。对于每一个child,则是将delegate中的getConstraintsForChild设置的约束条件,设置在child上。
Flow布局上的表现,受Delegate中getSize以及getConstraintsForChild两个方法的影响。第一个方法设置其尺寸,第二个方法设置其children的布局约束条件。
接下来我们来看一下其绘制方法。
void _paintWithDelegate(PaintingContext context, Offset offset) {_lastPaintOrder.clear();_paintingContext = context;_paintingOffset = offset;for (RenderBox child in _randomAccessChildren) {final FlowParentData childParentData = child.parentData;childParentData._transform = null;}try {_delegate.paintChildren(this);} finally {_paintingContext = null;_paintingOffset = null;}}
它的绘制方法非常的简单,先将上次设置的参数都初始化,然后调用delegate中的paintChildren进行绘制。在paintChildren中会调用paintChild方法去绘制每个child,我们接下来看下其代码。
@overridevoid paintChild(int i, { Matrix4 transform, double opacity = 1.0 }) {transform ??= new Matrix4.identity();final RenderBox child = _randomAccessChildren[i];final FlowParentData childParentData = child.parentData;_lastPaintOrder.add(i);childParentData._transform = transform;if (opacity == 0.0)return;void painter(PaintingContext context, Offset offset) {context.paintChild(child, offset);}if (opacity == 1.0) {_paintingContext.pushTransform(needsCompositing, _paintingOffset, transform, painter);} else {_paintingContext.pushOpacity(_paintingOffset, _getAlphaFromOpacity(opacity), (PaintingContext context, Offset offset) {context.pushTransform(needsCompositing, offset, transform, painter);});}}
paitChild函数首先会将transform值设在child上,然后根据opacity值,决定其绘制的表现。
- 当opacity为0时,只是设置了transform值,这样做是为了让其响应区域跟随调整,虽然不显示出来;
- 当opacity为1的时候,只是进行Transform操作;
- 当opacity大于0小于1时,先调整其透明度,再进行Transform操作。
至于其为什么高效,主要是因为它的布局函数不牵涉到child的布局,而在绘制的时候,则根据delegate中的策略,进行有效的绘制。
1.6 使用场景
Flow在一些定制化的流式布局中,有可用场景,但是一般写起来比较复杂,但胜在灵活性以及其高效。
2. Table
A widget that uses the table layout algorithm for its children.
2.1 简介
每一种移动端布局中都会有一种table布局,这种控件太常见了。至于其表现形式,完全可以借鉴其他移动端的,通俗点讲,就是表格。
2.2 布局行为
表格的每一行的高度,由其内容决定,每一列的宽度,则由columnWidths属性单独控制。
2.3 继承关系
Object > Diagnosticable > DiagnosticableTree > Widget > RenderObjectWidget > Table
2.4 示例代码
Table(columnWidths: const <int, TableColumnWidth>{0: FixedColumnWidth(50.0),1: FixedColumnWidth(100.0),2: FixedColumnWidth(50.0),3: FixedColumnWidth(100.0),},border: TableBorder.all(color: Colors.red, width: 1.0, style: BorderStyle.solid),children: const <TableRow>[TableRow(children: <Widget>[Text('A1'),Text('B1'),Text('C1'),Text('D1'),],),TableRow(children: <Widget>[Text('A2'),Text('B2'),Text('C2'),Text('D2'),],),TableRow(children: <Widget>[Text('A3'),Text('B3'),Text('C3'),Text('D3'),],),],)
一个三行四列的表格,第一三行宽度为50,第二四行宽度为100。

2.5 源码解析
构造函数如下:
Table({Key key,this.children = const <TableRow>[],this.columnWidths,this.defaultColumnWidth = const FlexColumnWidth(1.0),this.textDirection,this.border,this.defaultVerticalAlignment = TableCellVerticalAlignment.top,this.textBaseline,})
2.5.1 属性解析
columnWidths:设置每一列的宽度。
defaultColumnWidth:默认的每一列宽度值,默认情况下均分。
textDirection:文字方向,一般无需考虑。
border:表格边框。
defaultVerticalAlignment:每一个cell的垂直方向的alignment。
总共包含5种:
- top:被放置在的顶部;
- middle:垂直居中;
- bottom:放置在底部;
- baseline:文本baseline对齐;
- fill:充满整个cell。
textBaseline:defaultVerticalAlignment为baseline的时候,会用到这个属性。
2.5.2 源码
我们直接来看其布局源码:
第一步,当行或者列为0的时候,将自身尺寸设为0x0。
if (rows * columns == 0) {size = constraints.constrain(const Size(0.0, 0.0));return;}
第二步,根据textDirection值,设置方向,一般在阿拉伯语系中,一些文本都是从右往左现实的,平时使用时,不需要去考虑这个属性。
switch (textDirection) {case TextDirection.rtl:positions[columns - 1] = 0.0;for (int x = columns - 2; x >= 0; x -= 1)positions[x] = positions[x+1] + widths[x+1];_columnLefts = positions.reversed;tableWidth = positions.first + widths.first;break;case TextDirection.ltr:positions[0] = 0.0;for (int x = 1; x < columns; x += 1)positions[x] = positions[x-1] + widths[x-1];_columnLefts = positions;tableWidth = positions.last + widths.last;break;}
第三步,设置每一个cell的尺寸。
for (int x = 0; x < columns; x += 1) {final int xy = x + y * columns;final RenderBox child = _children[xy];if (child != null) {final TableCellParentData childParentData = child.parentData;childParentData.x = x;childParentData.y = y;switch (childParentData.verticalAlignment ?? defaultVerticalAlignment) {case TableCellVerticalAlignment.baseline:child.layout(new BoxConstraints.tightFor(width: widths[x]), parentUsesSize: true);final double childBaseline = child.getDistanceToBaseline(textBaseline, onlyReal: true);if (childBaseline != null) {beforeBaselineDistance = math.max(beforeBaselineDistance, childBaseline);afterBaselineDistance = math.max(afterBaselineDistance, child.size.height - childBaseline);baselines[x] = childBaseline;haveBaseline = true;} else {rowHeight = math.max(rowHeight, child.size.height);childParentData.offset = new Offset(positions[x], rowTop);}break;case TableCellVerticalAlignment.top:case TableCellVerticalAlignment.middle:case TableCellVerticalAlignment.bottom:child.layout(new BoxConstraints.tightFor(width: widths[x]), parentUsesSize: true);rowHeight = math.max(rowHeight, child.size.height);break;case TableCellVerticalAlignment.fill:break;}}}
第四步,如果有baseline则进行相关设置。
if (haveBaseline) {if (y == 0)_baselineDistance = beforeBaselineDistance;rowHeight = math.max(rowHeight, beforeBaselineDistance + afterBaselineDistance);}
第五步,根据alignment,调整child的位置。
for (int x = 0; x < columns; x += 1) {final int xy = x + y * columns;final RenderBox child = _children[xy];if (child != null) {final TableCellParentData childParentData = child.parentData;switch (childParentData.verticalAlignment ?? defaultVerticalAlignment) {case TableCellVerticalAlignment.baseline:if (baselines[x] != null)childParentData.offset = new Offset(positions[x], rowTop + beforeBaselineDistance - baselines[x]);break;case TableCellVerticalAlignment.top:childParentData.offset = new Offset(positions[x], rowTop);break;case TableCellVerticalAlignment.middle:childParentData.offset = new Offset(positions[x], rowTop + (rowHeight - child.size.height) / 2.0);break;case TableCellVerticalAlignment.bottom:childParentData.offset = new Offset(positions[x], rowTop + rowHeight - child.size.height);break;case TableCellVerticalAlignment.fill:child.layout(new BoxConstraints.tightFor(width: widths[x], height: rowHeight));childParentData.offset = new Offset(positions[x], rowTop);break;}}}
最后一步,则是根据每一行的宽度以及每一列的高度,设置Table的尺寸。
size = constraints.constrain(new Size(tableWidth, rowTop));
最后梳理一下整个的布局流程:
- 当行或者列为0的时候,将自身尺寸设为0x0;
- 根据textDirection进行相关设置;
- 设置cell的尺寸;
- 如果设置了baseline,则进行相关设置;
- 根据alignment设置cell垂直方向的位置;
- 设置Table的尺寸。
如果经常关注系列文章的读者,可能会发现,布局控件的布局流程基本上跟上述流程是相似的。
2.6 使用场景
在一些需要表格展示的场景中,可以使用Table控件。
3. Wrap
A widget that displays its children in multiple horizontal or vertical runs.
3.1 简介
看简介,其实Wrap实现的效果,Flow可以很轻松,而且可以更加灵活的实现出来。
3.2 布局行为
Flow可以很轻易的实现Wrap的效果,但是Wrap更多的是在使用了Flex中的一些概念,某种意义上说是跟Row、Column更加相似的。
单行的Wrap跟Row表现几乎一致,单列的Wrap则跟Row表现几乎一致。但Row与Column都是单行单列的,Wrap则突破了这个限制,mainAxis上空间不足时,则向crossAxis上去扩展显示。
从效率上讲,Flow肯定会比Wrap高,但是Wrap使用起来会方便一些。
3.3 继承关系
Object > Diagnosticable > DiagnosticableTree > Widget > RenderObjectWidget > MultiChildRenderObjectWidget > Wrap
从继承关系上看,Wrap与Flow都是继承自MultiChildRenderObjectWidget,Flow可以实现Wrap的效果,但是两者却是单独实现的,说明两者有很大的不同。
3.4 示例代码
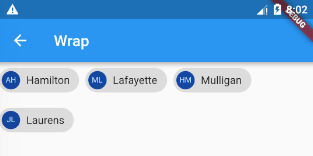
Wrap(spacing: 8.0, // gap between adjacent chipsrunSpacing: 4.0, // gap between lineschildren: <Widget>[Chip(avatar: CircleAvatar(backgroundColor: Colors.blue.shade900, child: new Text('AH', style: TextStyle(fontSize: 10.0),)),label: Text('Hamilton'),),Chip(avatar: CircleAvatar(backgroundColor: Colors.blue.shade900, child: new Text('ML', style: TextStyle(fontSize: 10.0),)),label: Text('Lafayette'),),Chip(avatar: CircleAvatar(backgroundColor: Colors.blue.shade900, child: new Text('HM', style: TextStyle(fontSize: 10.0),)),label: Text('Mulligan'),),Chip(avatar: CircleAvatar(backgroundColor: Colors.blue.shade900, child: new Text('JL', style: TextStyle(fontSize: 10.0),)),label: Text('Laurens'),),],)
示例代码直接使用的官方文档上的,效果跟Flow的例子中相似。
3.5 源码解析
构造函数如下:
Wrap({Key key,this.direction = Axis.horizontal,this.alignment = WrapAlignment.start,this.spacing = 0.0,this.runAlignment = WrapAlignment.start,this.runSpacing = 0.0,this.crossAxisAlignment = WrapCrossAlignment.start,this.textDirection,this.verticalDirection = VerticalDirection.down,List<Widget> children = const <Widget>[],})
3.5.1 属性解析
direction:主轴(mainAxis)的方向,默认为水平。
alignment:主轴方向上的对齐方式,默认为start。
spacing:主轴方向上的间距。
runAlignment:run的对齐方式。run可以理解为新的行或者列,如果是水平方向布局的话,run可以理解为新的一行。
runSpacing:run的间距。
crossAxisAlignment:交叉轴(crossAxis)方向上的对齐方式。
textDirection:文本方向。
verticalDirection:定义了children摆放顺序,默认是down,见Flex相关属性介绍。
3.5.2 源码
我们来看下其布局代码。
第一步,如果第一个child为null,则将其设置为最小尺寸。
RenderBox child = firstChild;if (child == null) {size = constraints.smallest;return;}
第二步,根据direction、textDirection以及verticalDirection属性,计算出相关的mainAxis、crossAxis是否需要调整方向,以及主轴方向上的限制。
double mainAxisLimit = 0.0;bool flipMainAxis = false;bool flipCrossAxis = false;switch (direction) {case Axis.horizontal:childConstraints = new BoxConstraints(maxWidth: constraints.maxWidth);mainAxisLimit = constraints.maxWidth;if (textDirection == TextDirection.rtl)flipMainAxis = true;if (verticalDirection == VerticalDirection.up)flipCrossAxis = true;break;case Axis.vertical:childConstraints = new BoxConstraints(maxHeight: constraints.maxHeight);mainAxisLimit = constraints.maxHeight;if (verticalDirection == VerticalDirection.up)flipMainAxis = true;if (textDirection == TextDirection.rtl)flipCrossAxis = true;break;}
第三步,计算出主轴以及交叉轴的区域大小。
while (child != null) {child.layout(childConstraints, parentUsesSize: true);final double childMainAxisExtent = _getMainAxisExtent(child);final double childCrossAxisExtent = _getCrossAxisExtent(child);if (childCount > 0 && runMainAxisExtent + spacing + childMainAxisExtent > mainAxisLimit) {mainAxisExtent = math.max(mainAxisExtent, runMainAxisExtent);crossAxisExtent += runCrossAxisExtent;if (runMetrics.isNotEmpty)crossAxisExtent += runSpacing;runMetrics.add(new _RunMetrics(runMainAxisExtent, runCrossAxisExtent, childCount));runMainAxisExtent = 0.0;runCrossAxisExtent = 0.0;childCount = 0;}runMainAxisExtent += childMainAxisExtent;if (childCount > 0)runMainAxisExtent += spacing;runCrossAxisExtent = math.max(runCrossAxisExtent, childCrossAxisExtent);childCount += 1;final WrapParentData childParentData = child.parentData;childParentData._runIndex = runMetrics.length;child = childParentData.nextSibling;}
第四步,根据direction设置Wrap的尺寸。
switch (direction) {case Axis.horizontal:size = constraints.constrain(new Size(mainAxisExtent, crossAxisExtent));containerMainAxisExtent = size.width;containerCrossAxisExtent = size.height;break;case Axis.vertical:size = constraints.constrain(new Size(crossAxisExtent, mainAxisExtent));containerMainAxisExtent = size.height;containerCrossAxisExtent = size.width;break;}
第五步,根据runAlignment计算出每一个run之间的距离,几种属性的差异,之前文章介绍过,在此就不做详细阐述。
final double crossAxisFreeSpace = math.max(0.0, containerCrossAxisExtent - crossAxisExtent);double runLeadingSpace = 0.0;double runBetweenSpace = 0.0;switch (runAlignment) {case WrapAlignment.start:break;case WrapAlignment.end:runLeadingSpace = crossAxisFreeSpace;break;case WrapAlignment.center:runLeadingSpace = crossAxisFreeSpace / 2.0;break;case WrapAlignment.spaceBetween:runBetweenSpace = runCount > 1 ? crossAxisFreeSpace / (runCount - 1) : 0.0;break;case WrapAlignment.spaceAround:runBetweenSpace = crossAxisFreeSpace / runCount;runLeadingSpace = runBetweenSpace / 2.0;break;case WrapAlignment.spaceEvenly:runBetweenSpace = crossAxisFreeSpace / (runCount + 1);runLeadingSpace = runBetweenSpace;break;}
第六步,根据alignment计算出每一个run中child的主轴方向上的间距。
switch (alignment) {case WrapAlignment.start:break;case WrapAlignment.end:childLeadingSpace = mainAxisFreeSpace;break;case WrapAlignment.center:childLeadingSpace = mainAxisFreeSpace / 2.0;break;case WrapAlignment.spaceBetween:childBetweenSpace = childCount > 1 ? mainAxisFreeSpace / (childCount - 1) : 0.0;break;case WrapAlignment.spaceAround:childBetweenSpace = mainAxisFreeSpace / childCount;childLeadingSpace = childBetweenSpace / 2.0;break;case WrapAlignment.spaceEvenly:childBetweenSpace = mainAxisFreeSpace / (childCount + 1);childLeadingSpace = childBetweenSpace;break;}
最后一步,调整child的位置。
while (child != null) {final WrapParentData childParentData = child.parentData;if (childParentData._runIndex != i)break;final double childMainAxisExtent = _getMainAxisExtent(child);final double childCrossAxisExtent = _getCrossAxisExtent(child);final double childCrossAxisOffset = _getChildCrossAxisOffset(flipCrossAxis, runCrossAxisExtent, childCrossAxisExtent);if (flipMainAxis)childMainPosition -= childMainAxisExtent;childParentData.offset = _getOffset(childMainPosition, crossAxisOffset + childCrossAxisOffset);if (flipMainAxis)childMainPosition -= childBetweenSpace;elsechildMainPosition += childMainAxisExtent + childBetweenSpace;child = childParentData.nextSibling;}if (flipCrossAxis)crossAxisOffset -= runBetweenSpace;elsecrossAxisOffset += runCrossAxisExtent + runBetweenSpace;
我们大致梳理一下布局的流程。
- 如果第一个child为null,则将Wrap设置为最小尺寸,布局结束;
- 根据direction、textDirection以及verticalDirection属性,计算出mainAxis、crossAxis是否需要调整方向;
- 计算出主轴以及交叉轴的区域大小;
- 根据direction设置Wrap的尺寸;
- 根据runAlignment计算出每一个run之间的距离;
- 根据alignment计算出每一个run中child的主轴方向上的间距
- 调整每一个child的位置。
3.6 使用场景
对于一些需要按宽度或者高度,让child自动换行布局的场景,可以使用,但是Wrap可以满足的场景,Flow一定可以实现,只不过会复杂很多,但是相对的会灵活以及高效很多。
4. 后话
笔者建了一个Flutter学习相关的项目,Github地址,里面包含了笔者写的关于Flutter学习相关的一些文章,会定期更新,也会上传一些学习Demo,欢迎大家关注。
5. 参考
- Flow class
- Table class
- Wrap class