- Middlewares
- Configuration Example
- Provider Namespace
- Available Middlewares
Middlewares
Tweaking the Request
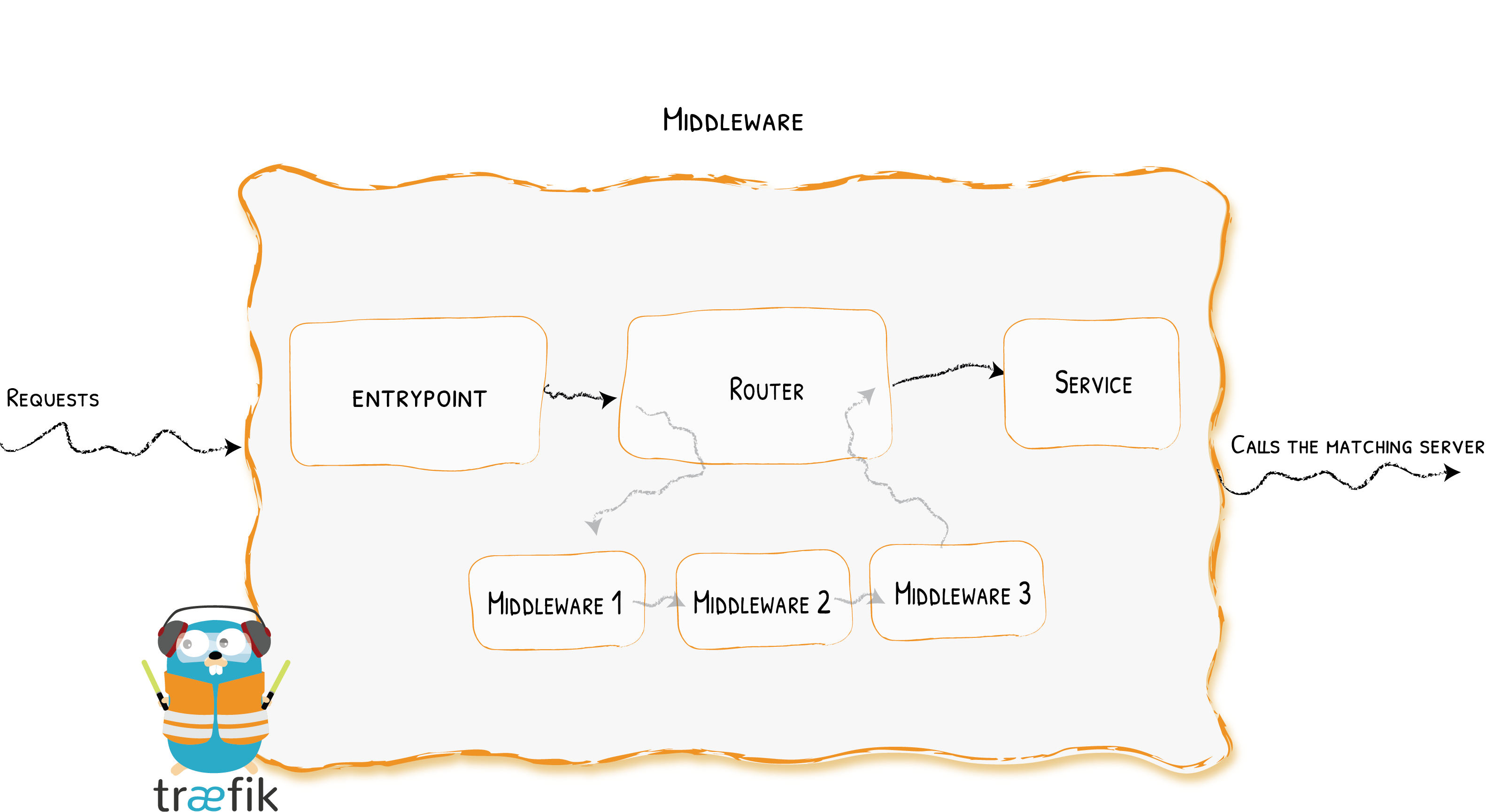
Attached to the routers, pieces of middleware are a mean of tweaking the requests before they are sent to your service (or before the answer from the services are sent to the clients).
There are many different available middlewares in Traefik, some can modify the request, the headers, some are in charge of redirections, some add authentication, and so on.
Pieces of middleware can be combined in chains to fit every scenario.
Configuration Example
# As a Docker Labelwhoami:# A container that exposes an API to show its IP addressimage: containous/whoamilabels:# Create a middleware named `foo-add-prefix`- "traefik.http.middlewares.foo-add-prefix.addprefix.prefix=/foo"# Apply the middleware named `foo-add-prefix` to the router named `router1`- "[email protected]"
# As a Kubernetes Traefik IngressRouteapiVersion: apiextensions.k8s.io/v1beta1kind: CustomResourceDefinitionmetadata:name: middlewares.traefik.containo.usspec:group: traefik.containo.usversion: v1alpha1names:kind: Middlewareplural: middlewaressingular: middlewarescope: Namespaced---apiVersion: traefik.containo.us/v1alpha1kind: Middlewaremetadata:name: stripprefixspec:stripPrefix:prefixes:- /stripit---apiVersion: traefik.containo.us/v1alpha1kind: IngressRoutemetadata:name: ingressroutespec:# more fields...routes:# more fields...middlewares:- name: stripprefix
"labels": {"traefik.http.middlewares.foo-add-prefix.addprefix.prefix": "/foo","traefik.http.routers.router1.middlewares": "[email protected]"}
# As a Rancher Labellabels:# Create a middleware named `foo-add-prefix`- "traefik.http.middlewares.foo-add-prefix.addprefix.prefix=/foo"# Apply the middleware named `foo-add-prefix` to the router named `router1`- "[email protected]"
# As TOML Configuration File[http.routers][http.routers.router1]service = "myService"middlewares = ["foo-add-prefix"]rule = "Host(`example.com`)"[http.middlewares][http.middlewares.foo-add-prefix.addPrefix]prefix = "/foo"[http.services][http.services.service1][http.services.service1.loadBalancer][[http.services.service1.loadBalancer.servers]]url = "http://127.0.0.1:80"
# As YAML Configuration Filehttp:routers:router1:service: myServicemiddlewares:- "foo-add-prefix"rule: "Host(`example.com`)"middlewares:foo-add-prefix:addPrefix:prefix: "/foo"services:service1:loadBalancer:servers:- url: "http://127.0.0.1:80"
Provider Namespace
When you declare a middleware, it lives in its provider namespace.For example, if you declare a middleware using a Docker label, under the hoods, it will reside in the docker provider namespace.
If you use multiple providers and wish to reference a middleware declared in another provider(aka referencing a cross-provider middleware),then you'll have to append to the middleware name, the @ separator, followed by the provider name.
<resource-name>@<provider-name>
Kubernetes Namespace
As Kubernetes also has its own notion of namespace, one should not confuse the "provider namespace"
with the "kubernetes namespace" of a resource when in the context of a cross-provider usage.In this case, since the definition of the middleware is not in kubernetes,specifying a "kubernetes namespace" when referring to the resource does not make any sense,and therefore this specification would be ignored even if present.
Referencing a Middleware from Another Provider
Declaring the add-foo-prefix in the file provider.
[http.middlewares][http.middlewares.add-foo-prefix.addPrefix]prefix = "/foo"
http:middlewares:add-foo-prefix:addPrefix:prefix: "/foo"
Using the add-foo-prefix middleware from other providers:
your-container: #image: your-docker-imagelabels:# Attach [email protected] middleware (declared in file)- "[email protected]e"
apiVersion: traefik.containo.us/v1alpha1kind: IngressRoutemetadata:name: ingressroutestripprefixspec:entryPoints:- webroutes:- match: Host(`bar.com`)kind: Ruleservices:- name: whoamiport: 80middlewares:- name: [email protected]# namespace: bar# A namespace specification such as above is ignored# when the cross-provider syntax is used.
Available Middlewares
| Middleware | Purpose | Area |
|---|---|---|
| AddPrefix | Add a Path Prefix | Path Modifier |
| BasicAuth | Basic auth mechanism | Security, Authentication |
| Buffering | Buffers the request/response | Request Lifecycle |
| Chain | Combine multiple pieces of middleware | Middleware tool |
| CircuitBreaker | Stop calling unhealthy services | Request Lifecycle |
| Compress | Compress the response | Content Modifier |
| DigestAuth | Adds Digest Authentication | Security, Authentication |
| Errors | Define custom error pages | Request Lifecycle |
| ForwardAuth | Authentication delegation | Security, Authentication |
| Headers | Add / Update headers | Security |
| IPWhiteList | Limit the allowed client IPs | Security, Request lifecycle |
| InFlightReq | Limit the number of simultaneous connections | Security, Request lifecycle |
| PassTLSClientCert | Adding Client Certificates in a Header | Security |
| RateLimit | Limit the call frequency | Security, Request lifecycle |
| RedirectScheme | Redirect easily the client elsewhere | Request lifecycle |
| RedirectRegex | Redirect the client elsewhere | Request lifecycle |
| ReplacePath | Change the path of the request | Path Modifier |
| ReplacePathRegex | Change the path of the request | Path Modifier |
| Retry | Automatically retry the request in case of errors | Request lifecycle |
| StripPrefix | Change the path of the request | Path Modifier |
| StripPrefixRegex | Change the path of the request | Path Modifier |